Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
2C (psychedelics)
Family of phenethylamine psychedelics From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
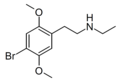
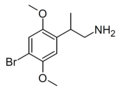
2C (2C-x) is a general name for the family of psychedelic phenethylamines containing methoxy groups on the 2 and 5 positions of a benzene ring.[1][2][3] Most of these compounds also carry lipophilic substituents at the 4 position, usually resulting in more potent and more metabolically stable and longer acting compounds.[4]

Most of the early 2C drugs were developed by Alexander Shulgin in the 1970s and 1980s and were reviewed in his 1991 book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines I Have Known And Loved).[3][5][6] 2C-B is the most popular of the 2C drugs.[3]
Remove ads
Use and effects
Summarize
Perspective
The 2C drugs are orally active, are used at oral doses of 6 to 150 mg depending on the drug, and have durations of 3 to 48 hours depending on the drug.[1][7][6][8] However, many have doses in the range of 10 to 60 mg and durations in the range of 4 to 12 hours.[1] The 2C drugs produce psychedelic effects, such as perceptual enhancement, psychedelic visuals, and euphoria.[1][6][9][3] Some, such as 2C-B, have also been reported to produce some entactogen-like effects, but findings in this area appear to be mixed.[9][3][10][11]
Remove ads
Interactions
The 2C drugs are metabolized by the monoamine oxidase (MAO) enzymes, including both MAO-A and MAO-B.[1][15] As a result, they may be potentiated by monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), such as phenelzine, tranylcypromine, moclobemide, and selegiline.[1][15][16] This may lead to overdose and serious toxicity.[1][15][16] There is no known reversal agent for 2C drugs, and medical management for overdose involves treatment of symptoms until toxicity within the body subsides.[17]
Remove ads
Pharmacology
Summarize
Perspective
Pharmacodynamics
Actions
The 2C drugs act as agonists of the serotonin 5-HT2 receptors, including of the serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptors.[18][19][20][21][22] They are partial agonists of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor.[18][19] Most of the 2C drugs have much lower affinity for the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor than for the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor.[18][19][20][21] Most of the 2C drugs have also shown about 5- to 15-fold higher affinity for the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor over the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor and about 15- to 100-fold higher affinity for the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor over the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor.[19] The psychedelic effects of the 2C drugs are thought to be mediated specifically by activation of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor.[18][20][22]
Unlike many other phenethylamines, 2C drugs, including 2C-C, 2C-D, 2C-E, 2C-I, and 2C-T-2 among others, are inactive as monoamine releasing agents and reuptake inhibitors.[18][23][20][19][22] Most of the 2C drugs are agonists of the rat and mouse trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1).[18][24][25][19] However, most are inactive as agonists of the human TAAR1.[18][24][25][19] The 2C drugs show very weak monoamine oxidase inhibition, including of monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and/or monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B).[18]
Effects
In accordance with their psychedelic effects in humans, the 2C drugs produce the head-twitch response and wet dog shakes, behavioral proxies of psychedelic effects, in rodents.[18] At least some 2C drugs, such as 2C-D and 2C-E, produce hyperlocomotion at lower doses in rodents.[18] All 2C drugs produce hypolocomotion at higher doses in rodents.[18] 2C drugs, including 2C-C, 2C-D, 2C-E, and 2C-I, substitute partially to fully for psychedelics like DOM, DMT, and LSD and/or for the entactogen MDMA in rodent drug discrimination tests.[18][20] However, none of the assessed 2C drugs substituted for dextromethamphetamine, suggesting that they lack amphetamine-type or stimulant-like effects.[18][20]
In contrast to most psychedelics, at least two assessed 2C drugs, 2C-C and 2C-P, have shown reinforcing effects in rodents, including conditioned place preference (CPP) and self-administration.[18][30] The mechanism by which these effects are mediated is unknown.[18] However, it may be related to reduced expression of the dopamine transporter (DAT) and increased DAT phosphorylation, in turn resulting in increased extracellular dopamine levels in certain brain areas.[18][30] These 2C drugs might have misuse potential in humans.[18][30] Similar reinforcing effects in animals have been observed for NBOMe analogues of 2C drugs, including 25B-NBOMe, 25D-NBOMe, 25E-NBOMe, 25H-NBOMe, and 25N-NBOMe.[18][31][32][33][34][35][36]
Similarly to DOI, tolerance has been found to gradually develop to the head-twitch response induced by 2C-T-7 with chronic administration in rodents.[18]
Various 2C drugs show potent anti-inflammatory effects mediated by serotonin 5-HT2A receptor activation.[37] Among these include 2C-I, 2C-B, 2C-H, and 2C-iBu.[37][38] Others, such as 2C-B-Fly and 2C-T-33, were less effective.[37] 2C-iBu has shown a greater separation between anti-inflammatory effects and psychedelic-like effects in animals than other 2C drugs and is being investigated for possible use as a pharmaceutical drug.[38][39]
Pharmacokinetics
The 2C drugs are orally active.[1] They are metabolized by O-demethylation and deamination.[1][15] This is mediated specifically by monoamine oxidase (MAO) enzymes MAO-A and MAO-B, whereas cytochrome P450 enzymes appear to metabolize only some 2C drugs and to have only a very small role.[15]
Remove ads
Chemistry
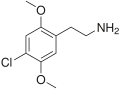
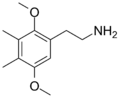
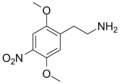
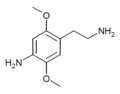
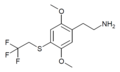
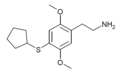
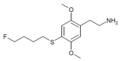
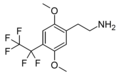
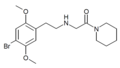
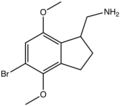
The 2C drugs, also known as 4-substituted 2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamines, are substituted phenethylamines and can be thought of as synthetic analogues of the naturally occurring phenethylamine psychedelic mescaline (3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine).[5][6][7][40][4] They are the phenethylamine (2C) analogues of the amphetamine (α-methylphenethylamine) DOx drugs like DOM, DOB, and DOI as well as of the phenylisobutylamine (α-ethylphenethylamine) 4C drugs like Ariadne (4C-D) and 4C-B.[6][7][40][4] The N-benzylphenethylamines such as 25I-NBOMe, 25B-NBOMe, and 25C-NBOMe are derivatives of the 2C drugs.[41][5][4] Certain FLY drugs such as 2C-B-FLY are also 2C derivatives.[5][4][2]
Syntheses
The chemical syntheses of 2C drugs have been described.[6][2]
Analysis
The chemical analysis of 2C drugs has been described.[5]
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
2,4,5-Trimethoxyphenethylamine (2,4,5-TMPEA; 2C-O), the 2C positional isomer of mescaline (3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine), was first synthesized by Max Jansen and was reported to produce psychedelic effects similar to those of mescaline in 1931.[42][43] However, subsequent studies in the 1960s and 1970s suggested that 2,4,5-TMPEA may actually be inactive as a psychedelic in animals and humans.[42]
2C-D was the first of the 2C drugs after 2C-O to be discovered.[2][44][45][46] It was synthesized and studied in animals by Beng T. Ho and colleagues at the Texas Research Institute of Mental Sciences and they published their findings in 1970.[2][44][45][46] Alexander Shulgin synthesized 2C-B and 2C-D in 1974 and discovered their psychedelic effects in self-experiments conducted in 1974 and 1975.[1][41][2][44][47][48] He published his findings in the scientific literature in 1975.[1][41][2][44][47] However, Shulgin had previously tested sub-threshold doses of 2C-D in 1964 and 1965.[49] 2C-T was first described by Shulgin and David E. Nichols in 1976.[50] 2C-I was first described by Shulgin and colleagues in 1977 and initial psychoactivity was reported by Shulgin in 1978.[42][51] Shulgin also first synthesized 2C-E in 1977.[52][53] He reviewed several of these 2C drugs in a literature review in 1979.[54] Subsequently, numerous other 2C drugs have been synthesized and characterized.[6][7][2][1][41] Shulgin comprehensively reviewed and described the 2C drugs in his 1991 book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines I Have Known and Loved).[6][3] He coined the term "2C", this term being an acronym for the two carbon atoms between the benzene ring and the amino group of the 2C drugs and a means to distinguish them from the three-carbon DOx drugs.[6][1][3]
2C-D was extensively studied by Hanscarl Leuner under the names DMM-PEA and LE-25 in psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy in Germany in the 1970s and 1980s.[41][55][56][57][58] It was also informally studied by Darrell Lemaire as a potential "smart drug" in the 1970s and 1980s.[59][60][61][62] He additionally developed the TWEETIO drugs such as 2CD-5-ETO via structural modification of the 2Cs.[59][60][61][62][40][7] 2C-B was legitimately marketed and sold as an over-the-counter sexual enhancer under brand names like Erox in several European countries such as Germany in the 1980s and early 1990s.[63][5][64][65] It was sold in adult stores, smart shops, and some nightclubs.[63][64]
2C-B was first encountered as a novel designer drug in the United States in 1979.[63] It gained popularity as a recreational drug and MDMA (ecstasy) alternative in the mid-1980s.[1][3][5] The drug became a controlled substance in the United States in 1994 or 1995.[1][3][5] It has been said to be the most popular of the 2C drugs in terms of recreational use.[3][5] Numerous other 2C drugs besides 2C-B have also since been made controlled substances.[5]
Remove ads
Society and culture
Legal status
Canada
As of October 12, 2016, the 2C-x family of substituted phenethylamines is a controlled substance (Schedule III) in Canada.[66]
List of 2C drugs
Remove ads
Related compounds
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads